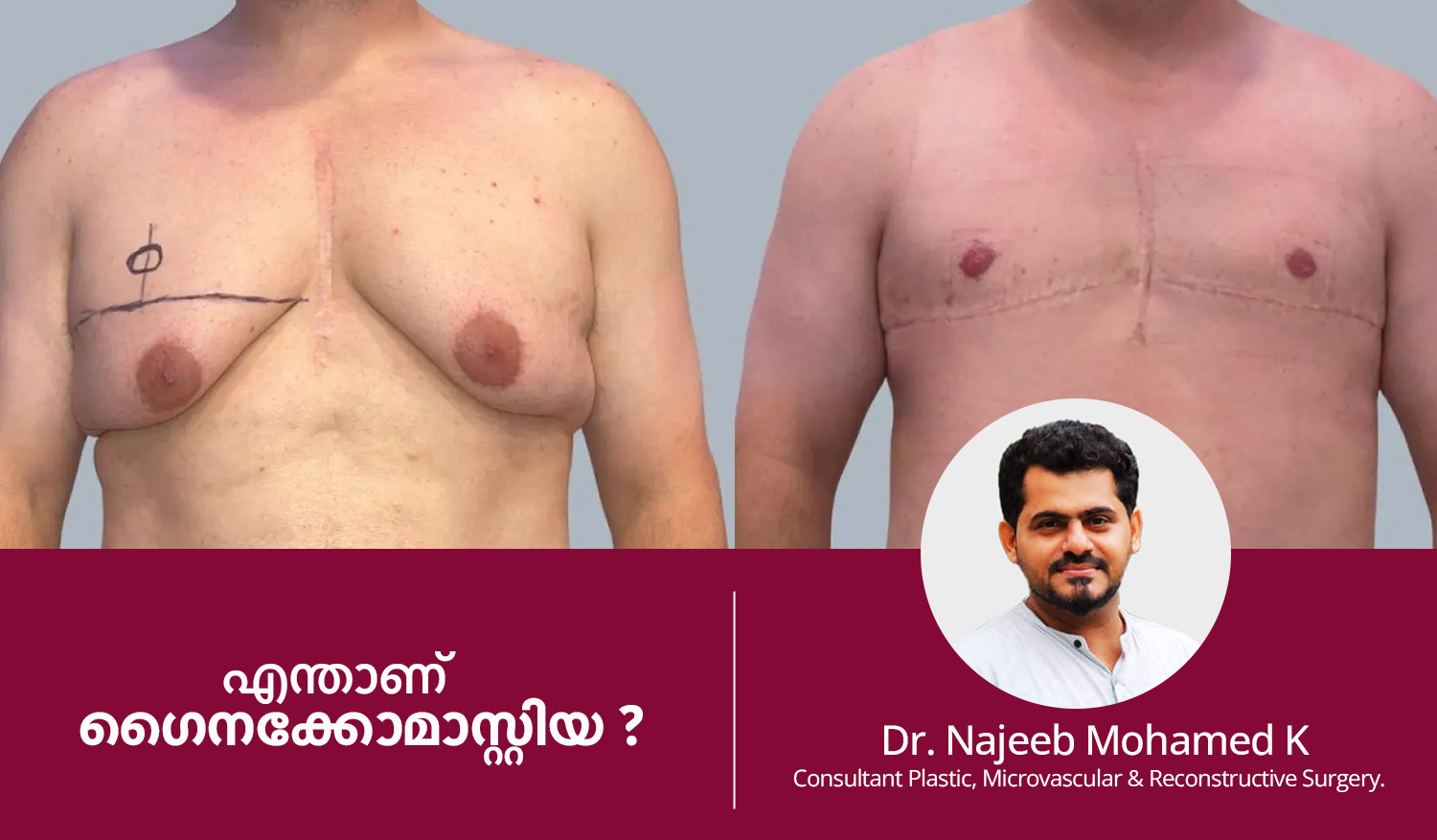
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a medical condition marked by the abnormal enlargement of breast tissue in males, resulting in swollen or glandular breasts, which can affect one or both sides. Although commonly benign, gynecomastia can cause physical and emotional discomfort for those affected.
The root cause of gynecomastia lies in an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone hormones. While hormonal fluctuations during puberty can cause temporary breast tissue growth, some individuals experience a persistent or late-onset imbalance, leading to more noticeable breast development.
Various factors contribute to gynecomastia, including hormonal shifts, specific medications, underlying medical conditions, or a combination of these elements. Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is essential for individuals dealing with gynecomastia to identify the specific cause and explore suitable management options.
While gynecomastia itself is generally not a serious medical issue, its impact on self-esteem and body image can be significant. Depending on the severity, treatment options may include lifestyle adjustments, hormonal therapies, or, in more extreme cases, surgical procedures.
It is imperative for those suspecting gynecomastia to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized guidance on the most appropriate course of action based on their individual circumstances.
How do I get a surgery to remove gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia removal surgery, while tailored to individual needs, is generally a well-established and routine procedure designed to address the natural variations in male chest anatomy. The complexity of the process depends on several factors, but it's essential to emphasize that for many individuals, it's a straightforward and highly successful journey towards achieving a more confident and comfortable self.
Recovery from gynecomastia removal surgery varies from person to person, but patients often experience some swelling, bruising, and discomfort, which typically subside over time. Most individuals can return to their normal activities within a week or two, although strenuous exercise may need to be avoided for a few weeks.
It's important for individuals considering gynecomastia removal surgery to consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon. The surgeon will assess their unique situation, discuss potential risks and benefits, and provide guidance on the most appropriate approach to achieve the desired results.
Liposuction
Liposuction is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to remove excess fat from specific areas of the body. The goal of liposuction is to reshape and contour the body by targeting localized fat deposits that may be resistant to diet and exercise. It is not a weight loss method but rather a way to address stubborn areas of fat that do not respond well to traditional weight loss efforts.
What happens in a liposuction procedure:
Consultation:
Before undergoing liposuction, individuals typically have a consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon evaluates the patient's overall health, discusses their goals, and determines if liposuction is an appropriate option.
Incisions:
Small incisions are made in the targeted area. These incisions are typically quite small, as the surgeon inserts a thin, hollow tube called a cannula through them.
Fat Removal:
The surgeon uses the cannula to suction out excess fat cells from beneath the skin. The cannula is moved back and forth to break up the fat deposits, making them easier to remove.
Closing Incisions:
Once the desired amount of fat has been removed, the surgeon closes the incisions with sutures. The incisions are usually very small and strategically placed to minimize scarring.
Recovery:
A compression garment may be worn to help reduce swelling and support the healing process.
Liposuction is commonly used on areas such as the abdomen, thighs, hips, buttocks, arms, and chin. It's important to note that liposuction is not a solution for obesity or a substitute for a healthy lifestyle. Ideal candidates are individuals who are at or near their target weight but have localized areas of fat that are resistant to diet and exercise.
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications associated with liposuction. It's crucial for individuals considering liposuction to consult with a qualified and experienced plastic surgeon who can assess their specific situation, discuss realistic expectations, and provide personalized guidance.
Abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty, commonly known as a tummy tuck, is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to improve the appearance of the abdominal area. It involves the removal of excess skin and fat, as well as the tightening of abdominal muscles to create a smoother, firmer, and more aesthetically pleasing contour. Abdominoplasty is often sought by individuals who have experienced significant weight loss, pregnancy, or aging, and as a result, have excess skin and weakened abdominal muscles.
Here is an overview of the typical abdominoplasty procedure:
Consultation:
In order to undergo the procedure the patient has to firstly consult a certified plastic surgeon beforehand. The surgeon then assesses the patient's medical history, discusses their goals, and evaluates the condition of the abdominal area.
Incisions:
The surgeon makes incisions to access the abdominal area. The length and pattern of incisions depend on the extent of correction needed.
Removal of Excess Skin and Fat:
The surgeon lifts the skin and underlying tissue to access the abdominal muscles. Excess skin and fat are removed, and the remaining skin is re-draped over the abdominal area.
Repositioning of the Navel:
If necessary, the surgeon repositions the navel to maintain a natural appearance.
Closing Incisions:
The incisions are closed with sutures, and any excess fluid may be drained through temporary drainage tubes.
Recovery:
After surgery, patients typically wear a compression garment to minimize swelling and support the healing process.
Recovery time varies, but most individuals can return to light activities within a few weeks, with more strenuous activities gradually reintroduced.